Sorting and Searching
Contents
Sorting and Searching¶
Binary Search¶
def binary_search(arr, key):
"""
Assumes the arr is sorted in increasing order
O(logn) time complexity
"""
if len(arr) == 0 or key == arr[0]:
return 0
low = 0
high = len(arr)
while low <= high:
mid = low + (high - low) // 2
if arr[mid] < key:
low = mid + 1
elif arr[mid] > key:
high = mid - 1
else:
return mid
return -1
print(binary_search([4, 6, 10], 10))
print(binary_search([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7], 5))
print(binary_search([10, 11, 12], 2))
2
4
-1
Binary Search Application¶
See Python for binary search application using the bisect built-in
from collections import defaultdict
from bisect import bisect_right
class TimeMap:
# approach #1
# use a hashmap
# key: [(timestamp, value), (timestamp, value)]
# approach #2
def __init__(self):
self.lookup = defaultdict(list)
def set(self, key: str, value: str, timestamp: int) -> None:
# timestamp increases with each successive call,
# so we can just append and they will be sorted
# by timestamp in increasing order
# create two defaultdicts for timestamps and values
# we could use one lookup with a list of tuples
# where lookup[key] = [(timestamp, value), (timestamp1, value1)]
# but bisect only provides the key parameter in python 3.10+
self.lookup[key].append((timestamp, value))
def get(self, key: str, timestamp: int) -> str:
if self.lookup.get(key) is None:
return ""
# If the last (and greatest) timestamp for this key is smaller
# than the timestamp requested, return the last timestamp
if self.lookup[key][-1][0] < timestamp:
return self.lookup[key][-1][1]
low = 0
high = len(self.lookup[key]) - 1
while low <= high:
mid = low + (high - low) // 2
if self.lookup[key][mid][0] < timestamp:
low = mid + 1
elif self.lookup[key][mid][0] > timestamp:
high = mid - 1
else:
# found it, return the value
return self.lookup[key][mid][1]
# since low is 0, no values <= timestamp exist in the array for this key
if low == 0:
return ""
# the exact timestamp was not found, but since we completed binary search
# we know that all values < low are <= the desired timestamp,
# so we return the value just to the left of low
return self.lookup[key][low-1][1] # all values <= to timestamp are to the left of low
Master Theorem with explanation (pdf)
from IPython import display
display.Image("media/master_theorem.png")
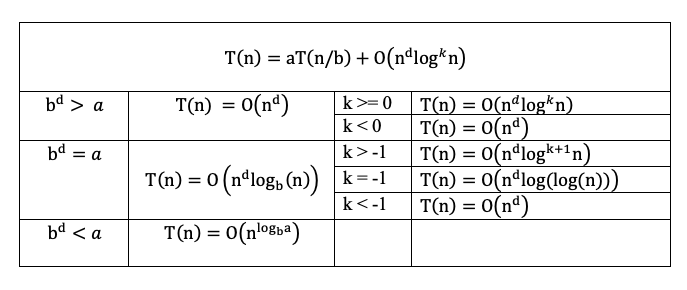
Mergesort (Divide and Conquer)¶
\(T(n) = aT(n/b) + O(n^{d}log^k{n})\)
a = number of subproblems in the recursion
n/b = the size of each subproblem
\(O(n^{d}log^k{n})\) = complexity of the merge
\(T(n) = 2T(n/2) + O(n) \)
therefore, \(b^d = a\) since b = 2, d = 1, a = 2
\(T(n) = O(nlogn)\)
def merge_sort(arr):
"""
The merge sort algorithm
"""
if len(arr) > 1:
# Finding the middle index of the array
n = len(arr)
A = arr[:n//2]
B = arr[n//2:]
# recursively sort each half.
# This breaks the problem down into two subproblems (a = 2) each of size (n/2), so b = 2
merge_sort(A)
merge_sort(B)
# i = the idx for iterating over A
# j = the idx for iterating over B
# k = the idx we are at in the merged array
i = j = k = 0
# arr is copied over to A[...] and B[...]
# so we overwrite
while i < len(A) and j < len(B):
if A[i] < B[j]:
arr[k] = A[i]
i += 1
else:
arr[k] = B[j]
j += 1
k += 1
# at this point either we've added all elements of A or B to the result, arr.
# we need to add the left over elements which are guaranteed to be both
# pre-sorted in increasing order and larger than the last element of arr
# add remaining elements from A
while i < len(A):
arr[k] = A[i]
i += 1
k += 1
# add remaining elements from B
while j < len(B):
arr[k] = B[j]
j += 1
k += 1
# Driver Code
arr = [12, 11, 13, 5, 6, 7]
print("Given array is")
print(arr)
merge_sort(arr)
print("Sorted array is: ")
print(arr)
Given array is
[12, 11, 13, 5, 6, 7]
Sorted array is:
[5, 6, 7, 11, 12, 13]
Mergesort application¶
Get max profit from array of prices
See other string / array solution here.
def max_profit(arr):
"""
Called recursively to find the max profit possible
of a single buy and sell order
@param arr: List[float] list of stock prices
@return: max profit, lowest price, highest price
"""
n = len(arr)
if n == 1:
return 0, arr[0], arr[0]
A = arr[:n//2]
B = arr[n//2:]
price_a, low_a, high_a = max_profit(A)
price_b, low_b, high_b = max_profit(B)
return max(price_a, price_b, high_b - low_a), min(low_a, low_b), max(high_a, high_b)
arr = [10, 12, 17, 3, 9]
profit, lowest_price, highest_price = max_profit(arr)
print(f"Prices: {arr}\n"
f"Max profit {profit},\n"
f"Lowest price: {lowest_price},\n"
f"Highest price: {highest_price}. ")
Prices: [10, 12, 17, 3, 9]
Max profit 7,
Lowest price: 3,
Highest price: 17.
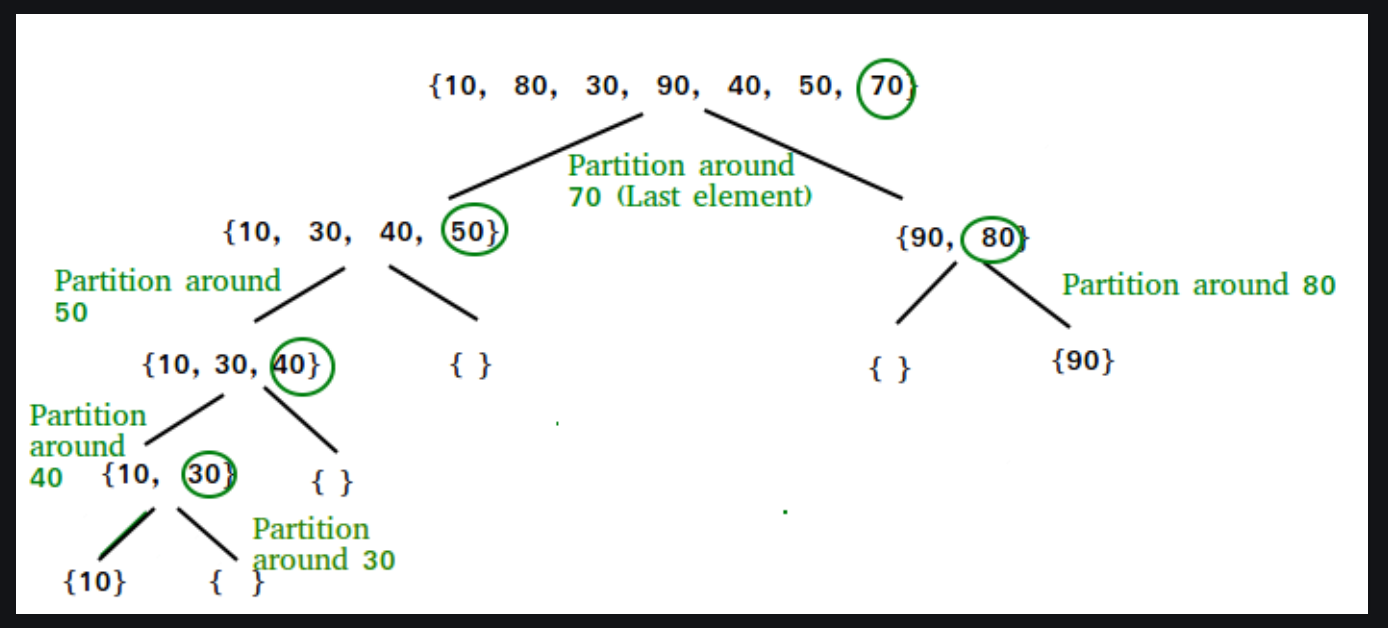
Quicksort (Divide and Conquer)¶
quicksort(arr, low, high):
"""
arr: array to sort
low: left index for sort, typically 0
high: right index for sort, typically last index in array
"""
if (low < high) //
pivot = partition(arr, low, high)
quicksort(arr, low, pivot - 1)
quicksort(arr, pivot + 1, high)
partition(arr, low, high)
"""rearranges arr from low to high in place"""
Sources:
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/quicksort-using-random-pivoting/
https://towardsdatascience.com/quicksort-in-python-dbefa7dcf9cc
from IPython import display
display.Image("media/quicksort.png")
from typing import List
import random
def partition_rand(arr: List[int], low: int, high: int):
# select a random pivot
pivot_idx = random.randrange(low, high)
# swap pivot and the last element to ensure
# pivot is the last element of the array
arr[high], arr[pivot_idx] = arr[pivot_idx], arr[high]
return partition(arr, low, high)
def partition(arr: List[int], low: int, high: int):
"""
Rearranges arr in place from low to high
"""
# partition around the last element
pivot_idx = high
pivot = arr[pivot_idx]
# i will hold first index of any element that is
# greater than or equal to the pivot
# initially, potentially no elements are greater
# than the pivot, so we set i = low - 1
i = low - 1
# move all elements less than the pivot
# to the left of the pivot
for j in range(low, high):
# if current elem is smaller than the pivot
if arr[j] < pivot:
i += 1
# we don't know what's at arr[i],
# but we know arr[j] is less than pivot
# swap elems at i and j and keep going
arr[i], arr[j] = arr[j], arr[i]
# now any elements starting at i + 1 are greater than
# or equal to the pivot
# move the pivot to i + 1
arr[i+1], arr[pivot_idx] = arr[pivot_idx], arr[i+1]
# the pivot now resides at index i + 1
return i + 1
def quicksort(arr, low, high):
"""
In-place sorting algorithm using a pivot
to partition elements
"""
if low < high:
# pivot index
# select a random pivot between low and high
pi = partition_rand(arr, low, high)
# choose arr[high] as the pivot
# pi = partition(arr, low, high)
quicksort(arr, low, pi - 1)
quicksort(arr, pi + 1, high)
a = [5,4,3,6,7,9]
quicksort(a, low=0, high=len(a)-1)
a
[3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9]
a = [9, -3, 5, 2, 6, 8, -6, 1, 3]
quicksort(a, low=0, high = len(a)-1)
a
[-6, -3, 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9]
Find median of two sorted arrays (mergesort application)¶
from typing import List
class Solution:
def findMedianSortedArrays(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> float:
# [1, 2, 3, 4]
# [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
# 1. Merged the sorted arrays into a single sorted array
# 2. If the # elements is even, return avg between two middle elements
# 3. If the # elements is odd, return the middle element
# Time: O(n+m) since we must iterate over both arrays
# Space: O(n+m) since we must store the merged array separately
if len(nums1) > len(nums2):
nums1, nums2 = nums2, nums1
# nums1 is the shortest length
n = len(nums1)
m = len(nums2)
is_even = False
if (n + m) % 2 == 0:
is_even = True
i = 0
j = 0
merged = []
while i < n and j < m:
if nums1[i] < nums2[j]:
merged.append(nums1[i])
i += 1
else:
merged.append(nums2[j])
j += 1
while i < n:
merged.append(nums1[i])
i += 1
while j < m:
merged.append(nums2[j])
j += 1
z = len(merged)
if is_even:
return (merged[(z // 2) - 1] + merged[z // 2]) / 2
return merged[z // 2]
Solution().findMedianSortedArrays([1,2], [3,4])
2.5
Solution().findMedianSortedArrays([1,3], [2])
2
Find median of two sorted arrays (binary search application)¶
class Solution:
def findMedianSortedArrays(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> float:
"""
Source: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=q6IEA26hvXc&t=510s
Time complexity: O(log(n+m))
Space complexity: O(1)
1. Finding a pivot point where all elements to the left are smaller and all
elements to the right are greater, you can find the median
x x [x]|[x] x x long_l, long_r
y [y]|[y] y short_l, short_r
x x [y] [x] | [y] y [x] x x
2. Any pivot point in the smaller array has a corresponding point on the
large array, that divides the total # of elements in two
x x x x x x
y y y y
3. After picking a pivot point, it's possible to determine whether we need to
go left or right
1 2 3|4 5 6
2 3|4 5
Code Outline
1. Binary search on small array
2. Get indices of long_l, long_r, short_l, short_r
3. Get direction we need to do binary search in (left (-1) or right (1) or 0 means we've found the right pivot)
4. At the end, calculate the median
"""
if len(nums1) > len(nums2):
nums1, nums2 = nums2, nums1
n = len(nums1)
m = len(nums2)
total = n + m
half = total // 2
# binary search over best pivot in nums1
# pivot in nums2 is determined from pivot in nums1
low = 0
high = len(nums1) - 1
while True:
mid_nums1 = low + (high - low) // 2
mid_nums2 = half - mid_nums1 - 2
short_l = nums1[mid_nums1] if mid_nums1 >= 0 else float("-inf")
short_r = nums1[mid_nums1+1] if mid_nums1+1 < n else float("inf")
long_l = nums2[mid_nums2] if mid_nums2 >= 0 else float("-inf")
long_r = nums2[mid_nums2+1] if mid_nums2+1 < m else float("inf")
# if partition is correct, determine result
if short_l <= long_r and long_l <= short_r:
if total % 2 == 0:
# determine two middle elements and then calculate their average
return (max(short_l, long_l) + min(short_r, long_r)) / 2
# odd: it's the smaller element of the right hand partitions
# 1|2 3
# 1|2
# 1 1 2 2 3
return min(short_r, long_r)
elif short_l > long_r:
# x x [x]|[x] x x long_l, long_r
# y [y]|[y] y short_l, short_r
high = mid_nums1 - 1
elif long_l > short_r:
# x x [x]|[x] x x long_l, long_r
# y [y]|[y] y short_l, short_r
low = mid_nums1 + 1
Solution().findMedianSortedArrays([1,2], [3,4])
2.5
Solution().findMedianSortedArrays([1,3], [2])
2
1146. Snapshot Array¶
Implement a SnapshotArray that supports the following interface:
SnapshotArray(int length) initializes an array-like data structure with the given length. Initially, each element equals 0. void set(index, val) sets the element at the given index to be equal to val. int snap() takes a snapshot of the array and returns the snap_id: the total number of times we called snap() minus 1. int get(index, snap_id) returns the value at the given index, at the time we took the snapshot with the given snap_id
Example 1:
Input: ["SnapshotArray","set","snap","set","get"]
[[3],[0,5],[],[0,6],[0,0]]
Output: [null,null,0,null,5]
Explanation:
SnapshotArray snapshotArr = new SnapshotArray(3); // set the length to be 3
snapshotArr.set(0,5); // Set array[0] = 5
snapshotArr.snap(); // Take a snapshot, return snap_id = 0
snapshotArr.set(0,6);
snapshotArr.get(0,0); // Get the value of array[0] with snap_id = 0, return 5
from pprint import pprint
import bisect
from collections import defaultdict
class SnapshotArray:
# Keep track of history of each element in a dictionary mapping
# indexes to a list of snap_ids and values:
# {
# 0: [[0, 0], [0, 3]],
# 1: [[0, 0], [0, 2]],
# 2: [[0, 0]],
#}
def __init__(self, length: int):
self.snapshots = defaultdict(list)
for i in range(length):
self.snapshots[i] = [[0, 0]]
self.snap_id = 0
def set(self, index: int, val: int) -> None:
self.snapshots[index].append([self.snap_id, val])
def snap(self) -> int:
ans = self.snap_id
self.snap_id += 1
return ans
def get(self, index: int, snap_id: int) -> int:
# O(logn) - binary search
# Get the idx of the last occurrence of the requested snap_id
# by getting the first index where all elements are less than snap_id + 1
# and then subracting one from that index
idx_last_snap_id = bisect.bisect(self.snapshots[index], [snap_id + 1]) - 1
return self.snapshots[index][idx_last_snap_id][1]
# Your SnapshotArray object will be instantiated and called as such:
# obj = SnapshotArray(length)
# obj.set(index,val)
# param_2 = obj.snap()
# param_3 = obj.get(index,snap_id)
a = SnapshotArray(length=3)
a.set(0, 1)
a.set(0, 2)
a.set(1, 2)
pprint(a.snapshots)
defaultdict(<class 'list'>,
{0: [[0, 0], [0, 1], [0, 2]],
1: [[0, 0], [0, 2]],
2: [[0, 0]]})
arr = [20, 21, 22, 22, 23, 24]
# ^ we need the last index of the snapshot in the SnapshotArray class above
idx_greater_than_x = bisect.bisect(arr, x=22)
idx_greater_than_x
4
idx_last_val_of_x = bisect.bisect(arr, x=22) - 1
idx_last_val_of_x
3
Search an element in a sorted and rotated array¶
Source: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/search-an-element-in-a-sorted-and-pivoted-array/
Input: arr[] = {5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 1, 2, 3}; key = 3
Output: Found at index 8
Approach
Find the pivot point with binary search. It’s the only index where the next element is smaller
Divide the array into two sub-arrays
Perform binary search
class Solution:
@staticmethod
def find_pivot(arr: List[int]) -> int:
"""
Finds index where dropoff occurs
e.g. 3,4,5,1,2 would return 2 since that is the index of the pivot, 5
"""
low = 0
high = len(arr) - 1
n = len(arr)
while low <= high:
mid = low + (high - low) // 2
if mid + 1 < n and arr[mid] > arr[mid + 1]:
# found pivot at mid
return mid
elif mid - 1 > 0 and arr[mid] < arr[mid - 1]:
# found pivot at mid - 1
return mid-1
elif arr[low] >= arr[mid]:
# element furthest left >= element at mid, set high one less than mid
# drop-down is left so search left
high = mid - 1
else:
# element further right < element at mid, set low to one above mid
# drop down is right so search right
low = mid + 1
return -1
def search(self, arr: List[int], key: int) -> int:
if len(arr) < 1:
return -1
if len(arr) == 1:
if arr[0] == key:
return 0
else:
return -1
pivot = Solution.find_pivot(arr)
if arr[pivot] < key or arr[pivot+1] > key:
return -1
if pivot == -1:
low = 0
high = len(arr) - 1
elif arr[0] <= key:
low = 0
high = pivot
else:
low = pivot+1
high = len(arr) - 1
if arr[low] == key:
return low
while low <= high:
mid = low + (high - low) // 2
if arr[mid] < key:
low = mid + 1
elif arr[mid] > key:
high = mid - 1
else:
return mid
return -1
print(Solution().find_pivot([3,4,5,1,2]))
print(Solution().find_pivot([2,3,4,5,1]))
print(Solution().find_pivot([5,1,2,3,4]))
print(Solution().find_pivot([0,1,2,3,4]))
a = [3,4,5,1,2]
print(f"Index of {1} in {a} is {Solution().search(a, 1)}")
a = [2,3,4,5,1]
print(f"Index of {1} in {a} is {Solution().search(a, 1)}")
a = [5,1,2,3,4]
print(f"Index of {1} in {a} is {Solution().search(a, 1)}")
a = [0,1,2,3,4]
print(f"Index of {1} in {a} is {Solution().search(a, 1)}")
a = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2]
print(f"Index of {0} in {a} is {Solution().search(a, 0)}")
2
3
0
-1
Index of 1 in [3, 4, 5, 1, 2] is 3
Index of 1 in [2, 3, 4, 5, 1] is 4
Index of 1 in [5, 1, 2, 3, 4] is 1
Index of 1 in [0, 1, 2, 3, 4] is 1
Index of 0 in [4, 5, 6, 7, 0, 1, 2] is 4
Bubble Sort¶
Repeatedly swap elements until they are all in place Time Complexity (Worst): O(n^2), Worst case occurs when array is reverse sorted. Best time Complexity: O(n) when the array is already sorted Space Complexity: O(1)
Source: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/bubble-sort/
def bubble_sort(arr):
n = len(arr)
for i in range(n):
swapped = False
for j in range(0, n-i-1):
if arr[j] > arr[j+1]:
arr[j], arr[j+1] = arr[j+1], arr[j]
swapped = True
if not swapped:
break
return arr
bubble_sort([8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1])
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
Insertion Sort¶
Algorithm:
Iterate over the array
Compare the current element to its predecessor
While the current element is less than it’s predecessor, swap left
Time complexity: O(n^2) Space complexity: O(1)
Source: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/insertion-sort/
def insertion_sort(arr: List[int]) -> List[int]:
n = len(arr)
for i in range(n):
j = i-1
while j >= 0 and arr[j] > arr[i]:
arr[i], arr[j] = arr[j], arr[i]
i -= 1
j -= 1
return arr
insertion_sort([9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1])
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
Insertion Sort Linked List Example Problem¶
https://leetcode.com/problems/insertion-sort-list/
from typing import Optional
# Definition for singly-linked list.
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
class Solution:
def insertionSortList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
# Time Complexity: O(n^2)
# Space Complexity: O(1)
# Insertion sort
# for each node, while it's greater than the previous node swap it (right) with the previous node
# head 5, 1, 3, 2
# result
# head 1, 3, 2 head 3, 2 head 2 head
# result 5 result 1, 5 result 1, 3, 5 result 1, 2, 3, 5
result = ListNode()
curr = head
while curr:
prev = result
# iterate over the resultant linked list and
# find the first position to insert the node there
# where the current node is greater
while prev.next and prev.next.val < curr.val:
prev = prev.next
tmp = curr.next
# insert the current node into the resultant linked list between prev and prev.next
# point prev -> curr -> prev.next
curr.next = prev.next
prev.next = curr
curr = tmp
return result.next
head = ListNode(5)
head.next = ListNode(4)
head.next.next = ListNode(3)
head.next.next.next = ListNode(2)
head.next.next.next.next = ListNode(1)
print(id(head))
result = Solution().insertionSortList(head)
print(id(result))
while result:
print(result.val)
result = result.next
4515373216
4515374368
1
2
3
4
5
834. Guess the Word¶
Source: https://leetcode.com/problems/guess-the-word/
# """
# This is Master's API interface.
# You should not implement it, or speculate about its implementation
# """
# class Master:
# def guess(self, word: str) -> int:
class Solution:
def findSecretWord(self, wordlist: List[str], master: 'Master') -> None:
# Observations
# If we get back a score of 0, eliminate all words that share > 0 letter positions in common with the last guessed word
# If we get back a score of 6, have our answer
# If we get back a score of 1-5, the correct word will have the same number of letter positions in common with the
# last guessed word as what was returned as the score.
# Approach
# 1. Make a function that filters the wordslist by the words that have
# at least x number of exact value and position matches as the input word
# 2. Guess a random word from the wordlist
def get_matches(word1: str, word2: str) -> bool:
# len(word1) == len(word2) since all words are of length 6
n = len(word1)
result = 0
for i in range(n):
if word1[i] == word2[i]:
result += 1
return result
random.seed(100)
for _ in range(10):
guess = wordlist[random.randint(0, len(wordlist) - 1)]
score = master.guess(guess)
if score == 6:
return guess
i = 0
while i < len(wordlist):
matches = get_matches(guess, wordlist[i])
if score == 0 and matches > 0:
wordlist.pop(i)
elif 0 < score < 6 and matches != score:
wordlist.pop(i)
else:
i += 1
